Standard algorithms
When writing programs they often use standard types of algorithms to sore and process data.
Stacks and queues
Stacks and queues allow the program to organise arrays using a protocol which define how the items are stored in the array.
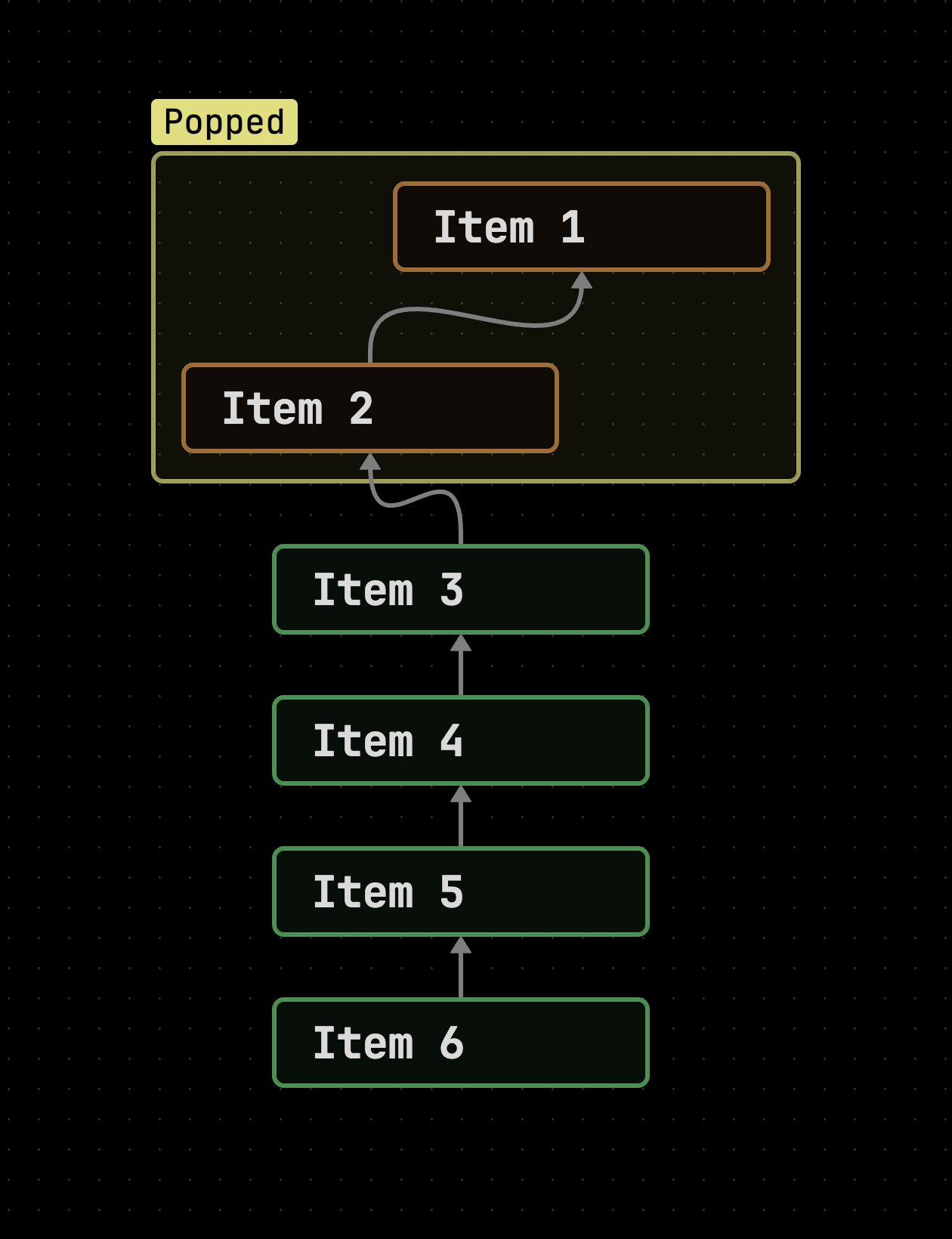
Stack
A stack uses the LIFO (Last in first out) data structure and has two basic operations.
- Push
- Pull
Data movement
Data in a stack must follow the last in first out protocol. If a item is added onto the array it gets put to the top of the array and if a item is removed then the top most item is removed.
Queue
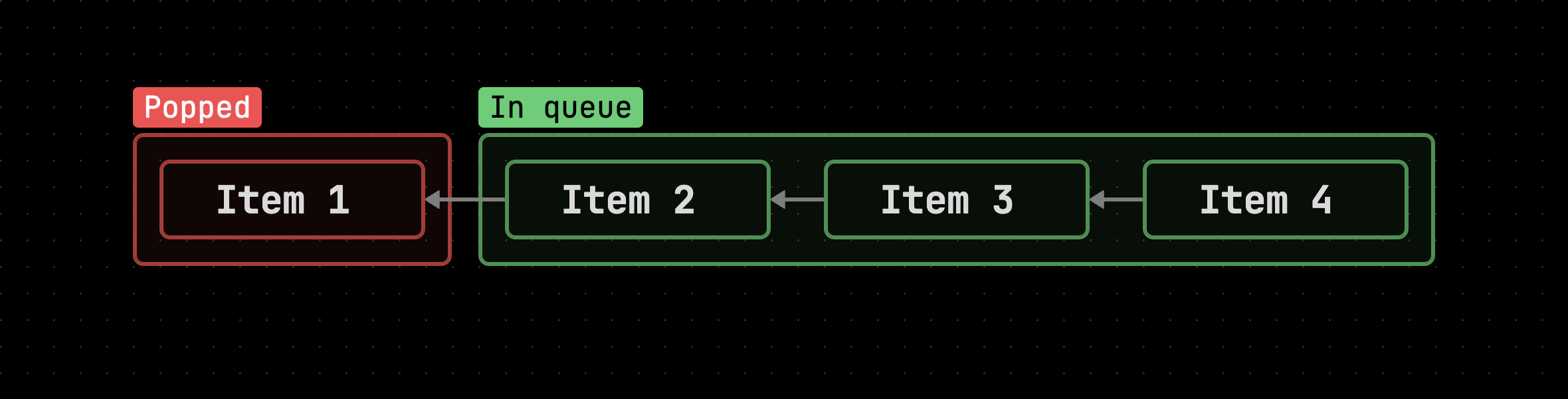
A queue uses the FIFO (First in first out) data structure and also has two basic functions.
- Push
- Pull
Data movement
Data in the queue must follow the first in first out protocol which means items in the data structure must keep moving left to the front.
Sorting algorithms
In programming sorting algorithms are programs that turn a unsorted array or list into a sorted one.
There are three main sorting algorithms:
- Bubble sort
- Insertion sort
- Quicksort
Bubble sort
Bubble sort is one of the most easiest sorting algorithms known. In a bubble sort a unsorted item keeps moving its way up the list until it is put in to the right position.
Each time a item is moved and reaches the correct place it is called a pass.
Insertion sort
Insertion sort is similar to bubble sort but it sorts using two sub lists. A sorted list and a unsorted list. The sort will loop trough each each item in the unsorted list and put in the correct order the sorted item
Quick sort
Quick sort is quite a complex sort where it splits the array in to partitions and sorts each partition. Once the partitions have been sorted the sort merges all the partitions all into one
Searches
Searching in programs allows the program to find items in lists and get the index of the item.
There are two main types of searches:
- Linear
- Binary
Linear
A linear search loops trough each item in the array until it hits the item in the array. A linear list
Binary search
Unlike a linear search the binary search must have a sorted list and the binary search works by splitting the list in half and deciding whether to look above or below the list. Then this process done again and again until the search has been found.